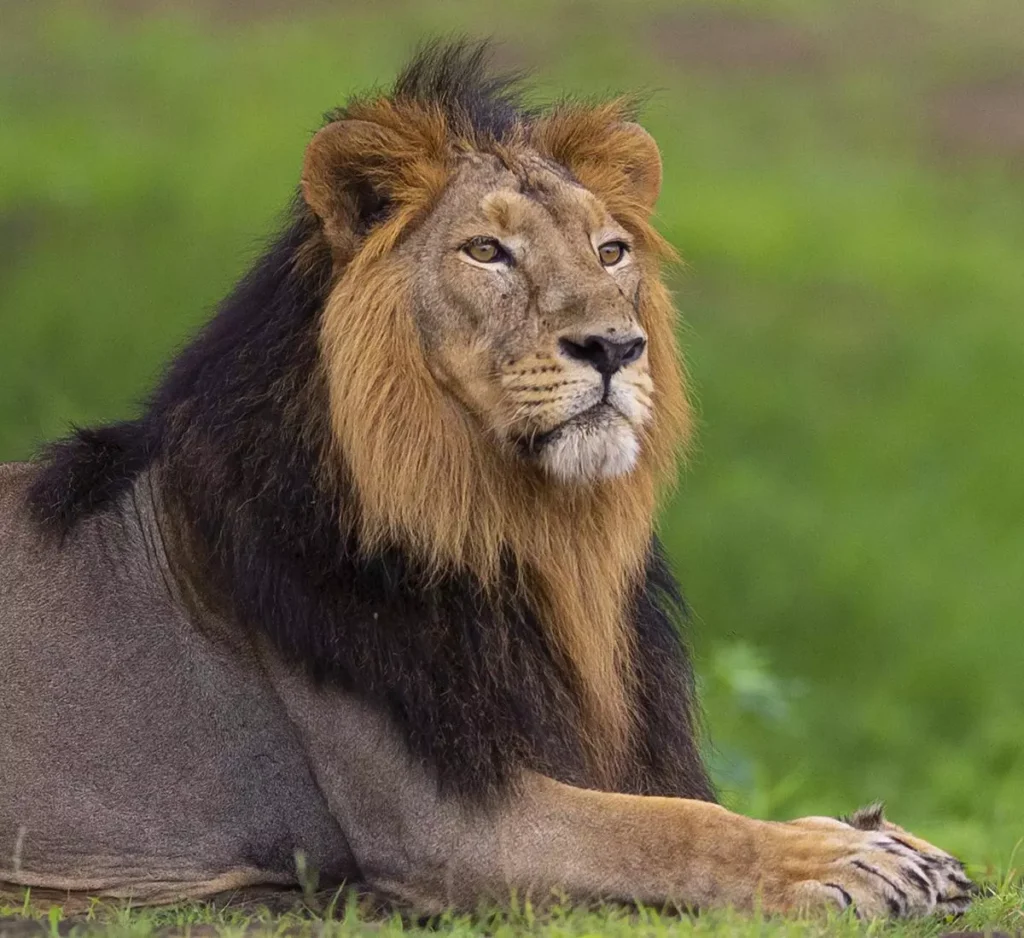
Physical Characteristics
- Size: Asian lions are generally slightly smaller than African lions. Males are larger than females, with an average shoulder height ranging from 1 meter to 1.1 meters.
- Color: Asian lions may have a tawny or yellowish-brown coat, often slightly paler than African lions.
- Structure: Asian lions typically have a robust build with thick legs and strong jaws, adapted for capturing prey and defending their territory.
Habitat and Distribution
Asian lions are primarily found in the western part of India, the Middle East, and some Central Asian regions. They inhabit various habitats, but they are typically associated with forested areas.
Behavior and Social Structure
- Social Groups: Asian lions often live in smaller social groups. These groups may consist of one male lion, several females, and their offspring. This social structure facilitates cooperation in activities such as hunting and territory defense.
- Hunting and Feeding: Asian lions are generally large game hunters, and their hunting strategies may vary based on the geographical region. They typically target prey such as deer, wild boars, and large ungulates.
Reproduction
The breeding season is usually focused on specific times of the year, but this can vary depending on the geographical region and population. Female lions have a gestation period of around 3 months and can give birth to 2 to 3 cubs on average.
Asian lions, like their African counterparts, play a crucial role in their ecosystems, and their conservation is important. However, they face threats such as habitat loss, hunting, and human-wildlife conflicts. Therefore, conservation efforts are crucial to ensuring the sustainable survival of Asian lions.